Discover what causes uterine fibroids to grow, their impact on health, and how they might affect fertility, pregnancy, and overall well-being.
Uterine fibroids are a prevalent concern for many women, especially during their reproductive years. While often non-cancerous, these growths can lead to discomfort and health complications. But have you ever wondered what causes uterine fibroids to grow? Understanding the factors behind their development can help you take proactive steps toward managing or even preventing them.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids, medically known as leiomyomas, are benign tumors that grow in or on the uterus. These growths can range in size from tiny, undetectable lumps to larger masses that distort the uterus.
How Common Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids affect up to 70-80% of women by the age of 50. However, not all fibroids cause symptoms, and their impact varies from person to person.
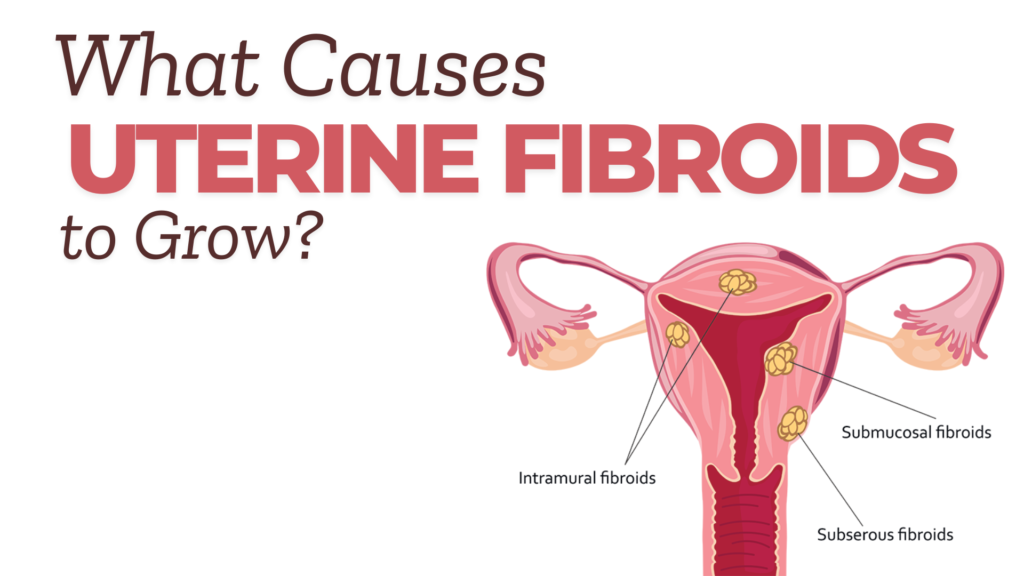
Types of Fibroids and Their Impact
- Intramural Fibroids: Found within the uterine wall.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Grow beneath the uterine lining.
- Subserosal Fibroids: Develop on the outer uterine wall.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: Attach to the uterus via a stalk.
Recognizing their type and location can help in understanding what causes uterine fibroids to grow and their potential symptoms.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids to Grow?
The exact causes of fibroid growth remain unclear, but research points to several contributing factors. Let’s explore these in detail:
1. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones like estrogen and progesterone play a significant role in fibroid growth. These hormones stimulate the growth of uterine tissue, indirectly promoting the formation of fibroids.
- During pregnancy, fibroids often grow due to elevated hormone levels.
- After menopause, fibroids tend to shrink because of reduced hormone production.
2. Genetics
If your mother, sister, or grandmother had fibroids, you’re more likely to develop them. Studies indicate that certain genetic mutations in uterine cells can trigger fibroid formation.
3. Lifestyle and Diet
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can influence what causes uterine fibroids to grow, including:
- High-fat diets: Increased consumption of red meat and processed foods has been linked to fibroid growth.
- Vitamin D deficiency: Low levels of Vitamin D may increase fibroid risk.
- Obesity: Higher body fat leads to elevated estrogen levels, creating a favorable environment for fibroids.
4. Inflammation and Toxins
Chronic inflammation and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (like phthalates) may trigger hormonal imbalances, increasing fibroid growth.
5. Pregnancy and Blood Flow
Pregnancy increases blood flow to the uterus, providing fibroids with nutrients and oxygen, which can accelerate their growth.
6. Insulin Resistance
Conditions like insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome can indirectly contribute to fibroid growth by disrupting hormonal balance.
Understanding these factors gives valuable insight into what causes uterine fibroids to grow and how to potentially minimize their impact.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
While fibroids can sometimes go unnoticed, they often manifest through a range of symptoms, including:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding that leads to anemia.
- Pelvic pain or pressure, especially with larger fibroids.
- Frequent urination due to pressure on the bladder.
- Constipation caused by fibroids pressing on the rectum.
- Difficulty conceiving or maintaining pregnancy, in some cases.
Knowing these symptoms is essential for early detection and management of what causes uterine fibroids to grow in your body.
Can Uterine Fibroids Cause Cancer?
Fibroids are almost always non-cancerous. However, in less than 1% of cases, a rare cancer called leiomyosarcoma can occur in the uterus. Importantly, leiomyosarcoma does not appear to develop from existing fibroids.
To ensure safety, regular check-ups and monitoring are crucial if you have fibroids.
How Do Uterine Fibroids Affect Fertility and Pregnancy?
1. Can Uterine Fibroids Cause Infertility?
Yes, fibroids can affect fertility by:
- Blocking the fallopian tubes.
- Distorting the uterine cavity, making implantation difficult.
- Reducing blood flow to the uterine lining.
2. Will Uterine Fibroids Affect Pregnancy?
Fibroids during pregnancy can lead to complications like:
- Preterm labor.
- Miscarriage.
- Placental abruption.
Despite these risks, many women with fibroids successfully carry healthy pregnancies.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
Managing fibroids begins with understanding what causes uterine fibroids to grow and choosing a treatment plan suited to your needs.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
- Medications: Hormonal therapy, like GnRH agonists, can shrink fibroids and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier diet and regular exercise can help slow fibroid growth.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE): Cuts off blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to destroy fibroids.
3. Surgical Interventions
- Myomectomy: Removes fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: A complete removal of the uterus, often used for severe cases.
Early intervention can prevent symptoms from worsening and help manage what causes uterine fibroids to grow effectively.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Fibroids
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce fibroid symptoms and possibly slow their growth:
- Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise reduces estrogen levels.
- Reduce Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Both can worsen hormonal imbalances.
These changes help address underlying factors contributing to what causes uterine fibroids to grow.
Conclusion
Understanding what causes uterine fibroids to grow is a vital step toward managing this common condition. While factors like hormones, genetics, and lifestyle play a role, there are numerous treatments and lifestyle adjustments to help women live healthier lives. Early detection and proactive management can make all the difference.
If you suspect fibroids or are experiencing symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
FAQs
Can uterine fibroids cause pain?
Yes, fibroids can cause pelvic pain, especially if they grow large or press on nearby organs.
Can uterine fibroids turn into cancer?
It is extremely rare. Fibroids are benign, and the likelihood of malignancy is less than 1%.
What causes uterine fibroids to grow?
Hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, lifestyle factors, and pregnancy-related changes are common causes.
How do uterine fibroids look like?
Fibroids appear as firm, white, rubbery nodules that vary in size, from tiny pea-sized growths to large masses.
Can uterine fibroids cause infertility?
Yes, fibroids can interfere with conception by blocking fallopian tubes or distorting the uterus.
Will uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
They can increase risks like preterm labor or miscarriage, but many women with fibroids have normal pregnancies.

